Published by: sadikshya
Published date: 02 Jul 2021
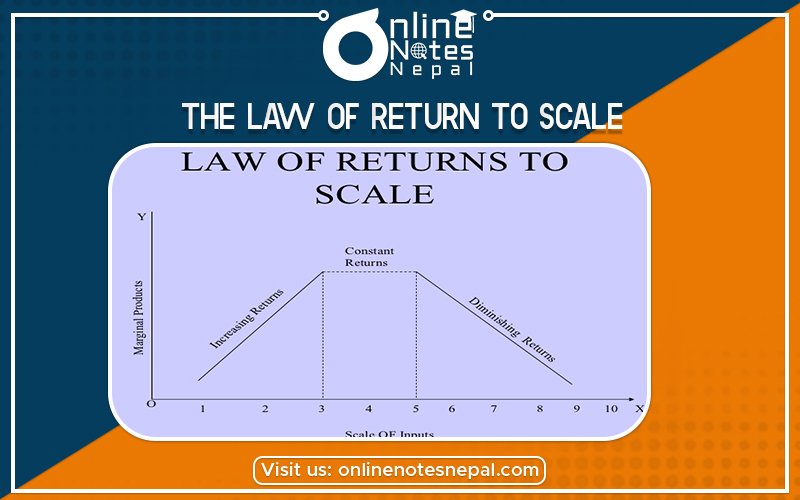
The law of return to scale describes the relationship between outputs and the scale of inputs. In the long run, where all inputs are increase or decrease in the same proportion, the law of return to scale is a long-run concept. In the long period, The law of return to scale describes the relationship between outputs and the scale of inputs. The firm can fire a large number of inputs or factors of production and change the scale of production. Therefore, in the long run, the firm can change the scale of operation and this production process is known as the law of returns to scale. According to Koutsoyiannis “The term return to scale refers to the change in input as all factors change by the same proportion”. There are three types of return to scale which can be explaining following.
If the output obtained from a production process increase at a faster rate than the rate of increase in inputs, the return to scale said to be increasing. Causes of increasing returns to scale are the specialization of labour. Machinery and technology indivisibility of factors of production etc. can be explained by the following table.
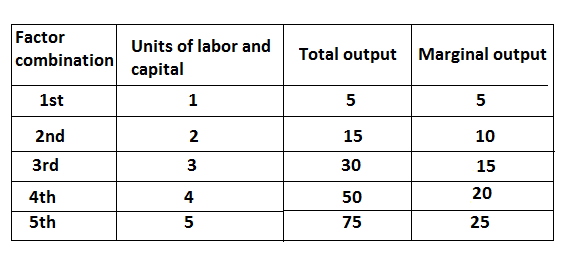
In this table output is an increase at a faster rate than the rate of increase in inputs. It can be explained by the following figure.
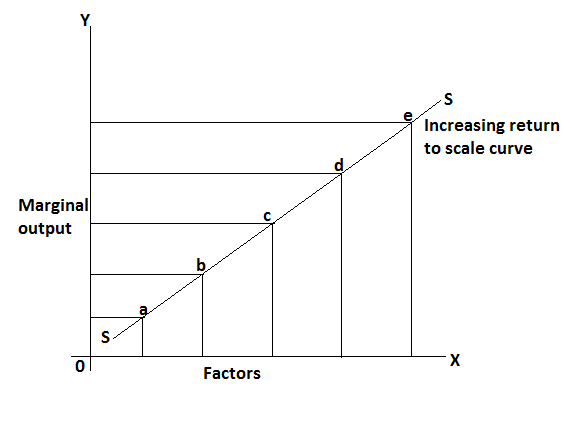
In this figure marginal production increase and also total production increase initially at an increasing rate.
The constant return to scale refers to the production situation in which output increases actually in the same proportion as a factor of production are increasing. In other words, if factors of production are double output will also be double, in this case, internal and external economics are exactly this economics. This situation arises when after reaching a certain level of production economics of scale are balanced of this economy of scale. In can be ex[lain by the following table.
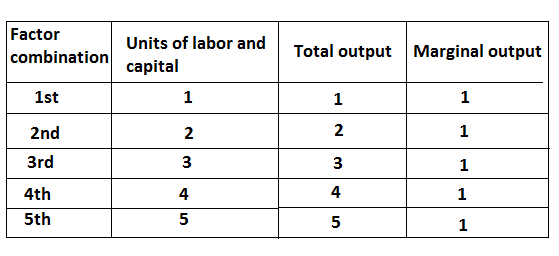
In this table, if factors of production are double output will also double which is known as constant return to scale. It can be explained by the following figure.
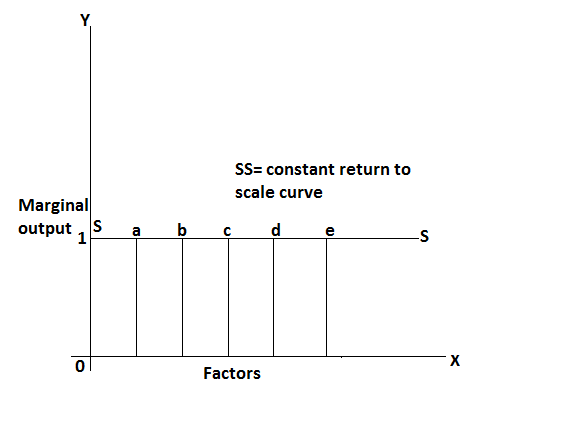
In this figure, marginal production constant and total production increases initially at a constant rate.
Decreasing to return to scale refers to the production situation in which output does not increase in the proportion of the increase in input the main causes of decreasing return to scale is increasing difficulty of management coordination and control. It can be explained by the following table.
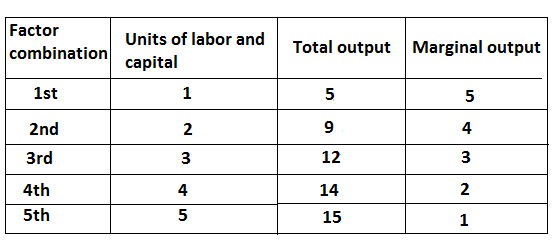
In the above table, the output is increased at a low rate than the rate of increase in inputs, which is known as decreasing return to scale. It can be explained by the following figure.
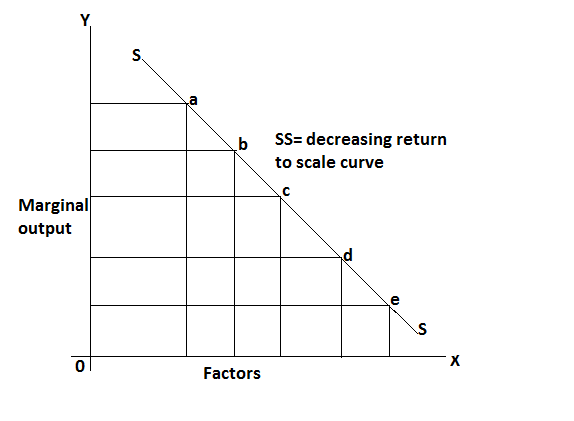
In this figure, marginal production decreases and total production increase initially at a decreasing rate.