Published by: sadikshya
Published date: 28 Jun 2021
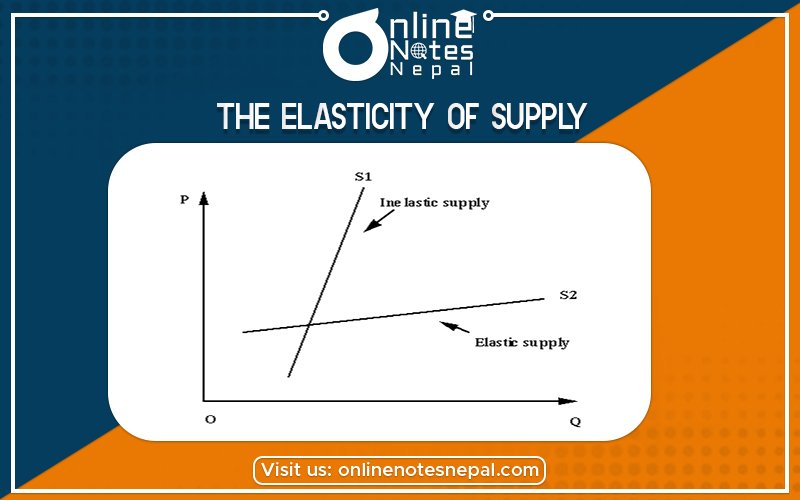
The elasticity of supply is a similar concept like elasticity of demand. It refers to the degree of changes in the quantity of supply in relation to change in price. Normally an increase in a price increase in supply but, the percentage of increase in supply may be equal to or more or less than the percentage increase in price. It can define as the degree of responsiveness of supply to a change in the price of a commodity. According to Samuelson elasticity of supply is the degree of responsiveness of supply of a commodity to a change in its price.
There are five types of elasticity of supply
perfectly inelastic supply
when there is no change in quantity supply in response to a change in price, it is known as perfectly inelastic supply or zero elasticity of supply. It can be explained by the following table.
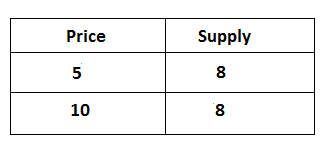
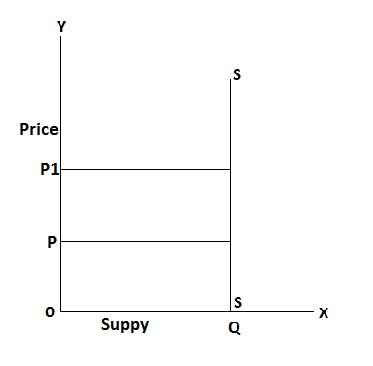
In the above table, the price of goods is Rs 5 and the supply of goods is 8 units in the initial state when the price of goods increase from Rs 5 to 10 but the supply of commodity remain same 8 units, that is called perfectly inelastic supply. It can be explained by the following figure.
If a small change in price brings infinity change in quantity supply is known as a perfectly elastic supply. In other words, if a seller will supply any quantity at the same price then it is also known as a perfectly elastic supply. It can be explained by the following table:
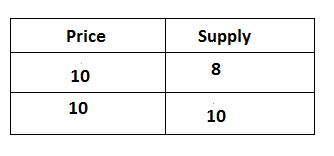
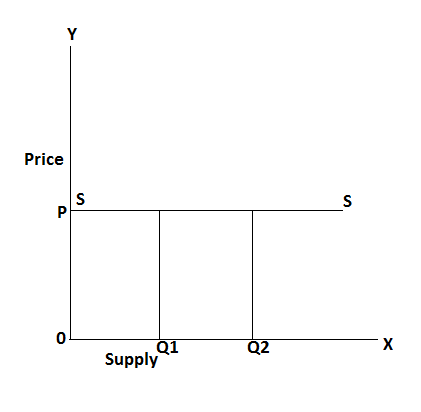
In the above table, the price of commodity Rs 10 and quantity supply of goods is 8 units in the beginning at the same price. Quantity of supply is increased from 8 to 10 units this situation is called perfectly elastic supply. It can be explained by the following figure:
The supply of goods is said to be elastic when the proportional change in quantity od supply is equal to the proportional change in price. it can be explained by the following table.
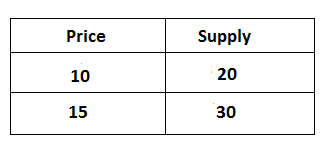
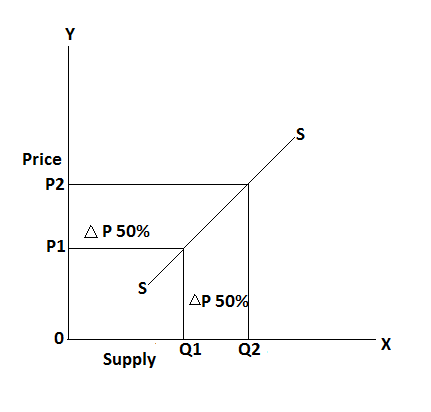
In the above table, the price of a commodity change from Rs 10 to 15 and a change in the quantity of supply is 20 to 30 units. It can be explained by the following figure:
If the supply of commodity changes more than the percentage change in price, the elasticity of supply is known as more than a unitary elastic supply. It can be explained by the following table.
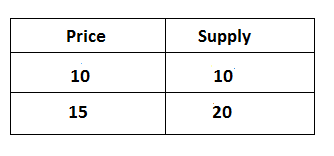
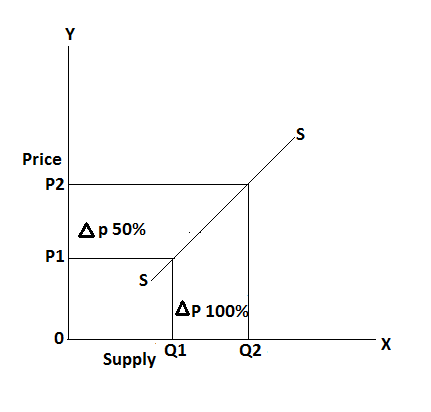
In the above table, the price of commodity changes from Rs 10 to 15 and the supply of a commodity is a change from 10 to 20 units, it shows that a 50% change in price leads 100% change in the supply of goods. It can be explained by the following figure:
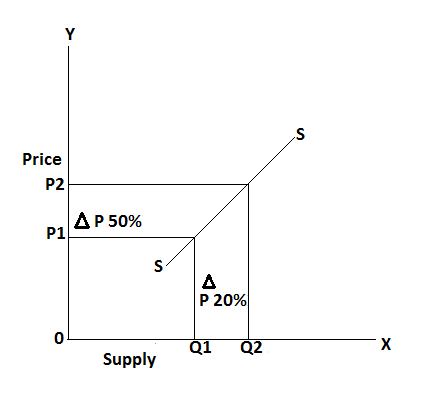
If a proportionate change in supply is less than the proportionate change in price then it is known as less than unitary elastic supply. It can be explained by the following table:
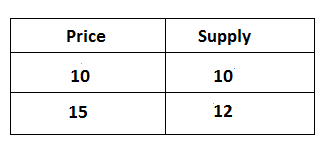
In the above table, the price of a commodity is changed from Rs 10 to 15 and the supply of the commodity is a change from 10 to 12 units, it shows that a 50% change in price affects 20% change in the supply of a commodity. It can be explained by the following figure: