Published by: sadikshya
Published date: 28 Jun 2021
The law of equi-marginal utility is originally produced by H.H Gossen and latter systemically developed by Marshall. It is known as various others names such as the law of substitute, the second law of Gossen, the law of maximum satisfaction, etc. this law guide the consumer to allocate his income among various commodity, in other to get in its maximum satisfaction.
This law state that a consumer is said to be in equilibrium if he spends his entire given money income on the purchase of various commodities such that the marginal utility of money expenditure on its commodity purchase is equal. This law is best on the following assumptions.
Under the above various assumptions, the law of equi-Marginal utility can be explained with the help of the following table.
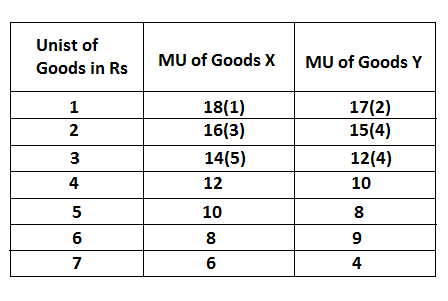
In the above table, the consumer reaches equilibrium, when he purchases four units of X goods and three units of Y goods because this combination satisfied the condition of equilibrium. It can be shown in the following figure.
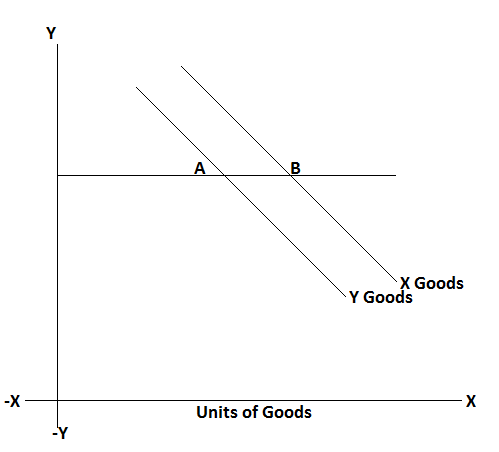
In this figure, when the consumer consumed four units of X goods and three units of Y goods. He gets equal (12, 12) marginal utility. It is a condition of maximum satisfaction of consumer equilibrium position.
In the field of consumption
Every consumer wants to get the maximum possible satisfaction out of his expenditure. Arranging is expenditure to that wants he must substitute the things of greater utility for one possessing less utility till MU’s is equalize. In this way, it serves as a guide to the consumer to affect the optimum allocation of his income expenditure. Thus it determines the relative demand for different goods.
In the field of production
Every producer aims at earning maximum profit to achieve his objective. He must utilize different factors of production such as land labour, capital, technology, etc. in such a way that the marginal productivity of each factor is equal. A producer must go on substituting one factor for the other till such time as the marginal productivity of each factor is equal. It is by this adjustment of limited resources that producers can succeed in his aim of getting maximum profit.
In the field of exchange
The principle of substitution can be applied in exchange. A person gives what he has in abundance in exchange for what is a source with him. He gives one commodity for another till MU of both became equal.
In the field of distribution
In distribution, we are concerned with the determination of the rewards of the various agents of production such as rent, wages, interest, and profit. Their shares are determined according to the principle of marginal productivity. Every factor of production is paid in proportion to its marginal productivity. Optimum distribution is obtained when all the actors get their wages in a proportion of their productivity.
In the field of public finance
It is also applicable in real finance. The government has limited income, it spends the amount on the public. Its expenditure should be such that society gets maximum benefits. Therefore government expenditure is guided by the principle of maximum social advantages.