Published by: sadikshya
Published date: 28 Jun 2021
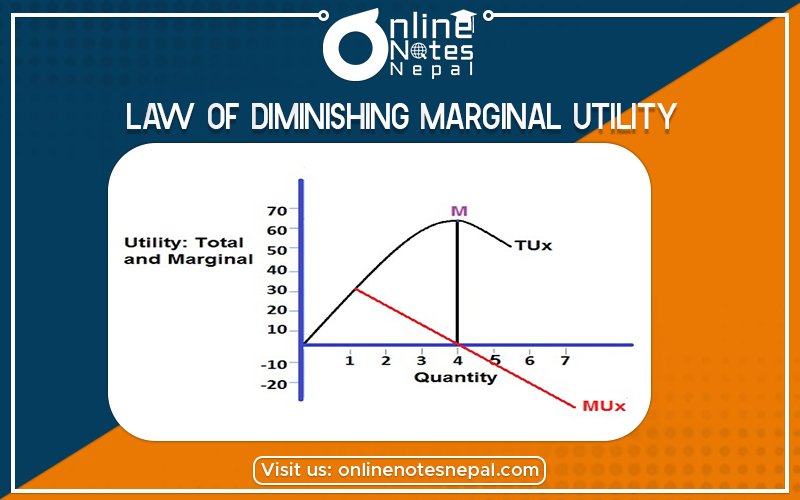
The law of diminishing marginal utility was first introduced by Gossen, therefore it is also known as the first law of Gossen. Later classical economist Marshall developed the law in a scientific way in his famous book “principle of economic”.
The diminishing marginal utility is generalization drawn from the characteristics of human wants. The wants of a human begin particular commodities diminishes as its consumption increases. This law tells us that we obtain less and less utility from the successive units of a commodity as we consumed more and more of it, for example, the wants of thirsty man for water is very strong but after he takes one glass of water his intensity of desire for another glass of water becomes less. According to K.E.Boulding “As a consumer increases the consumption of any one commodity, keeping constant, the consumptions of all other commodities the marginal utility of the various commodity must eventually. According to Marshall ” the additional benefit which a person derived from a given increase of his stock of anything diminishes with the growth of the stock he has”.
This law is best on the following assumption.
Under the above various assumptions, the law of diminishing marginal utility can be explained by the following table.
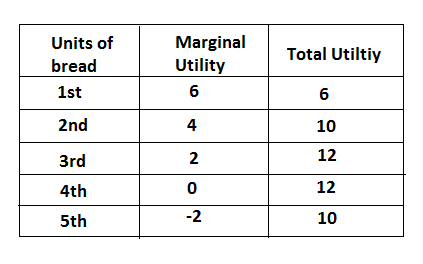
In the above table suppose a man-hungry he starts taking bread. The marginal utility which he gets from the first bread is 6, the second bread is 4, the third bread is 2 and 4th bread is zero. In each bread, he gets negative utility. The law of diminishing marginal utility has been explained by the following figure:
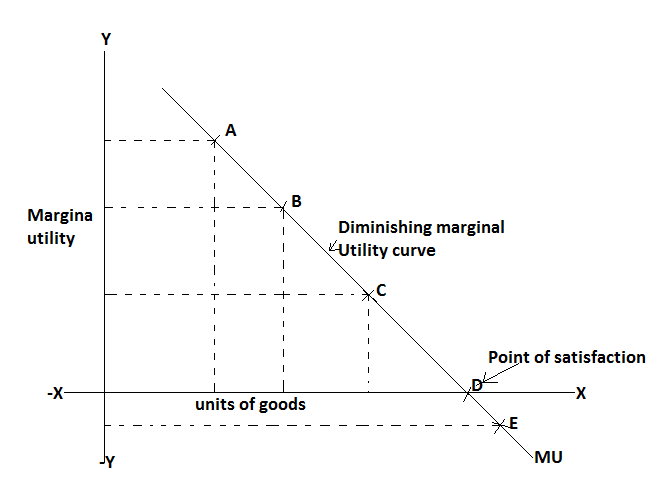
In this figure, MU is the marginal utility curve which shows downward left to right. When marginal utility is zero totals utility is maximum and the consumer will be equilibrium, so point D is called the point of maximum satisfaction. This point is also known as consumer equilibrium.
The following are the important exception or limitations to the law.
Rare collection
In the collection of curios and antiques, stamps old painting, coin, etc. This law does not apply because of marginal utility increase as the number of collection increases.
Money and misers
In this case of money and misers, this law does not apply because of the marginal utilities of money increase for the misers and the amount of money with the increase.
Conspicuous consumption
There are some people who love to display their possession of valuable goods. This person felt happier as the amount of such goods with them increases.
Craze
For people who are crazy about something, this law does not apply. People become happier if they have more of something about which they have developed of craze.
The limitations or exceptions mentioned above are more superficial than real, in fact, the law of diminishing marginal utility in economics is universal as the law of gravity in physics.