Published by: sadikshya
Published date: 28 Jun 2021
The neoclassical economist Marshall in 18190, in his book named principle of economic, propounds the law of demand. Does lower the price higher the quantity demand and higher the price lower the quantity demand. According to the Marshall “other thing remaining the same the amount, the demand increases with a fall in price and diminishes with a rise in price.
The law of demand is one of the most important laws of economic theory. According to the law of demand, another thing equal is the price of a commodity falls of the quantity demand rises quantity demand rise if the price of a commodity rises quantity for a want will decline. Thus there is an inverse relation between price quantity demands; other things are assumed to be equal or constant. The price of related goods, the income of the consumer, taste, and preference of consumer and such other factors that influence demand. If these factors which determine demand also undergo a change then the inverse relationship between price and demand may not holds goods. This law is explained on the basis of the following assumptions.
On the basis of the above assumption, the law of demand may be illustrated with the help of a demand schedule and demand curve.
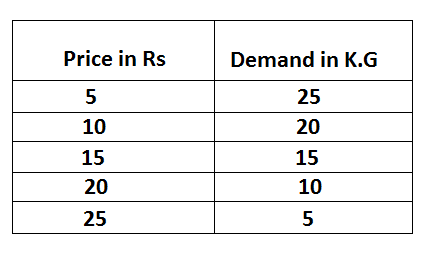
figure:
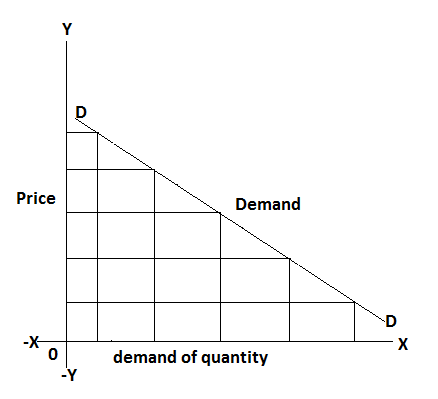
The above table, the diagram shows that the price and quantity demand of a product is inversely related. The demand curve (DD) is a downward slope from left to right decline when price increase quantity demand decrease and vice-versa.