Published by: Nuru
Published date: 17 Jan 2022
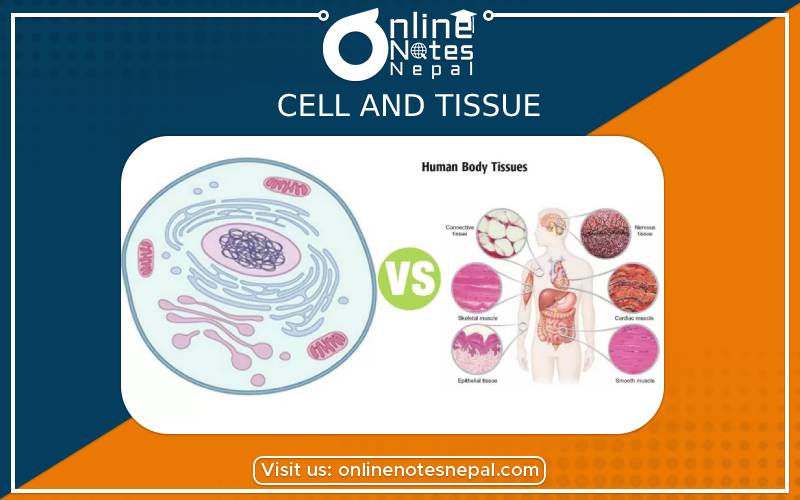
Cell is known as the structural and functional unit of life. A group of cells having similar structure and performing similar function are known as tissues. A group of tissues forms an organ which performs a single function.
Cells are generally divided into three parts:
a. Cell membrane:
Cell membrane is outer covering of the cell which is soft and thin. It consists of small pores through which important substance comes in and out of the cells. In plant cell, cell membrane is covered by cell wall made up of thick and strong cellulose.
b. Cytoplasm:
It is colorless, semipermeable liquid which is made up of carbohydrate fats and minerals. It contains:
Nucleus controls all the functions of the cell. They are covered by the nuclear membrane. Nucleus contains the fluid called nucleoplasmn and fibre shaped chromatins which are known as chromosomes. It contains the following importanat components:
| Plant cell | Animal cell |
| Centriole and centrosome are absent. | Centriole and centrosome are present except in invertebrates. |
| Its nucleus is pushed to one side by vacuole. | Its nucleus is located at the center. |
| Have plastids in them. | Usually plastids are absent in them. |
| Golgi bodies are smaller and scattered in cytoplasm. | Golgi bodies are bigger and found near nucleus in the form of a block. |
| It has a cellulosic cell wall surrounding plasma membrane. | The cell wall is absent. The cell is enclosed by the plasma membrane. |
| Mitochondria are usually fewer. | Mitochondria are usually numerous. |
| Usually plant cells are bigger and of regular shape. | Usually animal cells are smaller and have an irregular shape. |
A group of cells having similar structure and performing similar function are known as tissues.
In the animal tissues, there are five categories of tissues:
They are described below:
The group of cells which make outer covering of the body or its organ is known as epithelial tissue. This tissue looks like flat stones in surface view. The function of epithelial tissues are covering, protecting, secreting, excreting and absorbing. There are different types of epithelial tissues based on the nature and thickness of cells.
It is the muscular tissue that causes the movement of different parts of the body. All muscular tissues have great contractibility. This tissue consists of cellular elements in the form of fibers of various length which are called muscle fiber. Muscular tissues are of following types:
Connective tissue maintains a linkage among various other tissues in the body. Cells of such tissue remain scattered in different parts of the body and perform various functions. The main function of such tissue is to balance the body as well as connect various cells and tissues. There are intercellular spaces filled in with solid or liquid substances called matrix which contain water, fibers and minerals. On the basis of nature of tissue there are three types of connective tissues:
d. Nervous tissue
There is a particular organ that coordinates the functions of different organs in the animal body. This particular organ is the brain. Brain and spinal cord with a network of nerves constitute nervous system. Impulses are carried by nerves to the brain from the different parts of the body, similarly from the brain to different parts. This entire system is made of nervous tissue. Nervous tissue is made up of neuron. A neuron consists of nerve cell body and the fibers.
e. Liquid connective tissue
Blood is a liquid connective tissue. It transports various substances from one part to another. There are three types of blood corpuscles: red blood corpuscles, white blood corpuscles and platelets. These cells are found in floating in fluid called plasma. RBC contains hemoglobin that helps in transportation of oxygen in the body. WBC protects against infection and also helps in the transportation of various substances. Platelet helps the blood to clot, thus preventing the loss of blood from wounds and cuts.
Plant tissues are of two types:
Merismetic cells lies on the tip of growing plant which have thick cell wall, dense cytoplasm and clear nucleus .the tissue composed of these of this cells are called merismetic tissue .They help in the growth of the plants.
Primary meristems:
Those meristems, which are derived directly from the meristems of embryo and responsible for primary growth and lie mainly on the apices of stems and roots, are called primary meristems. They are apical meristems (root apical and shoot apical meristems), intercalary meristems (only in monocots). They help increase the length of the plant.
Secondary meristems:
They are the meristems which are formed as new meristems in permanent cells by re-differentiation and are responsible for increasing the diameter of the plant organ. They are of two types vascular cambium and cork cambium collectively known as lateral cambium (lateral meristem). They help plant to increase its girth. Secondary meristems are divided into three types which are as follows;
a. Apical meristems:
These meristems are found in the apices or the growing points of root and shoot.They help to increase the height of the plant.
b. Lateral meristems:
This meristem is found on the lateral side of stem and roots.They are found embedded in the permanent tissues. They are responsible for the increases in girthor diameter of the plant body. Vascular cambium and cork cambium are the examples of the lateral meristem.
c. Intercalary meristems:
These meristems lie between the permanent tissue as remains of apical meristems. They found at the base of the node or at the base of internodes or at the base of leaf or sheathing leaf of monocots. They are responsible for the increase of the length of the axis of plants.
The different types of permanent tissues found in the plants are as follows:
a. Simple tissue:
A simple permanent tissue consists of same kind of cells which perform a common function. This tissue, on the basis of structure is further classified into:
Parenchyma is found in all plants. This tissue consists of thin walled living cells. Parenchyma present is leaves contain chlorophyll and helps in the process of photosynthesis.
Collenchyma consists of elongated living cells with thick elastic cell wall. The main function of this tissue is to give mechanical support to the plant and help in photosynthesis.
The cell of sclerenchyma is dead or living with thick rigid walls. This tissue gives mechanical support to the plant.
b. Complex tissue
Complex permanent tissues are composed of different types of cells. These tissues differ in their structure and function but work collectively as single unit. This tissue is mainly of two types: Xylem and Phloem.
Xylem is composed of four types of dead cells: trachea, trachids, wood fiber and wood parenchyma. It is found in stem, root, leaf and the inner layer of other hard parts. It conducts water and minerals from the root to other parts and gives support to the plant. It stores water and food as well.
Phloem is made of living cells and s found in stem, root and leaf. It consists of different types of cells like sieve tube, companion cell and phloem parenchymal. Its main function is to conduct the food manufactured in leaves to various parts of the plants.
c. Special tissue
This issue includes glandular and lactiferous tissues made to perform function. Glandular tissues secrete various substances in solution form like oils, resin, gum, mucilage etc and are found in the plants like tobacco, pines, tulsi etc.
The plant body mainly consists root system and shoot system. The root system lies under the ground whereas the shoot lies above the ground. The root system and shoot system are made of different types of organs.
The root system is made of organs like root cap, root tip, lateral root etc. whereas shoot system is made of organs like leaves, stem, flower, fruit, buds etc. Again these organs are made of different types of tissues like parenchyma, (epidermis, cortex, endodermis, and pith), schlerenchyma (pericycle) xylem and phloem (vascular tissues etc.) pericycle, vascular tissues and pith are called stele group. And these tissues are made of different cells.