Published by: Nuru
Published date: 16 Jan 2022
Chemical bonding is the force of attraction that binds atoms or group of atoms to form a stable chemical molecule or compound. For example, hydrochloric acid (HCL) is formed of one molecule of hydrogen and one molecule of chlorine.
The chemical bond formed by the transfer of electrons from valence shell of an atom to the valence shell of another atom is called electrovalent bond and the valency is known as electrovalency.
Electrovalent bond is formed in between two atoms in which one atom belongs to metal and another is non-metal.
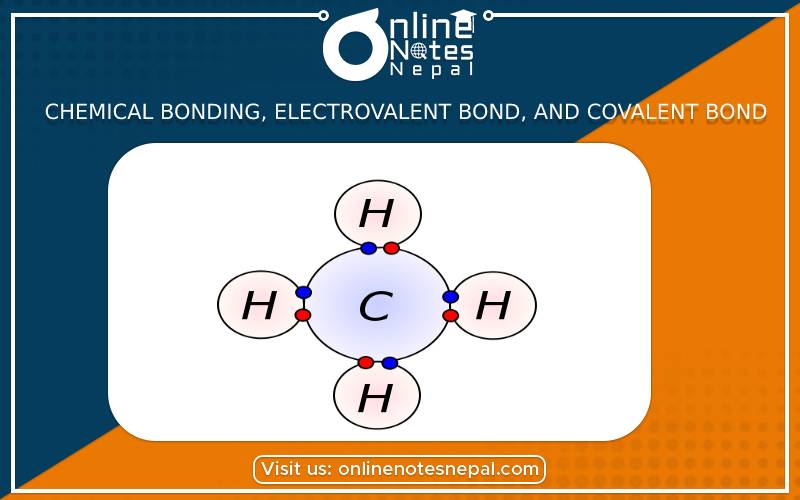
The covalent bond is formed by the sharing of a pair of electrons between two atoms each contributing an equal number of electrons to the electron pair
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Formula
Chemical Bonding:
Chemical bonding is the force of attraction that binds atoms or group of atoms to form a stable chemical molecule or compound. For example, hydrochloric acid (HCL) is formed of one molecule of hydrogen and one molecule of chlorine. The chlorine and hydrogen are found combined together due chemical bond. There are various type of chemical bonding. Here we study about two types of bonding which are given below,
Electrovalent bond:
The chemical bond formed by the transfer of electrons from valence shell of an atom to the valence shell of another atom is called electrovalent bond and the valency is known as electrovalency.
Electrovalent bond is formed in between two atoms in which one atom belongs to metal and another is non-metal. The metal atom loses its valence electron and gains positive ions or cation. On the other hand, non-metal atom gains an electron from metal to form stable negative ion or anion. Compounds like magnesium chloride, calcium oxide, sodium oxide, magnesium oxide and potassium chloride are formed by the electrovalent bonding.
Characteristics of electrovalent compounds are listed below:
Covalent bond
The covalent bond is formed by the sharing of a pair of electrons between two atoms each contributing an equal number of electrons to the electron pair. A covalent bond is represented by line (-) between the bonded atoms. When one pair of electron is shared, a single covalent bond is formed. Similarly, when two and three pairs of electrons are shared, they form double and triple bond respectively. Compounds like methane, ammonia, water and oxygen are formed by the covalent bonding.
Characteristics of covalent bond are listed below:
Molecular Formula:
A molecule is not a single atom but it is formed by the combination of two or more atoms of the same or different types in fixed proportion by their weight. Molecular formula is defined as the symbolic representation of the molecule of a substance. By observing the molecular formula, we can determine the no. of atoms involved in the formation of the molecule.
Molecular formula of an element: The molecular formula of an element is defined as the symbolic representation which shows the actual number of atoms in one molecule of the element.
Molecular formula of a compound: The molecular formula of a compound is defined as the symbolic representation which shows the actual number of an atom of different elements present in one molecule of the compound.
Information obtained from molecular formula are ;listed below in points:
Steps to write molecular formula:
To write the molecular formula of a molecule, we should follow the following steps given below,
Step 1: At first we should know the symbol and valences of elements and radicals present in a molecule.
Step 2: Write the name of the compounds
Step 3: Determine the basic and acidic charges
Step 4: Valency of one radical is transferred to another radical and is written on the right hand side at the bottom corner. If necessary, L.C.M. of the valencies is taken to get a simple whole number.
Step 4: When a compound radical is involved in molecular formula, the radical is enclosed in a bracket and the valency number is written on the right side of the bracket at the bottom of the formula.
For example; Calcium sulphate
Differences between symbol and molecular formula is shown in a T table:
| Symbol | Molecular formula |
| It is an abbreviation of the full name of an element. | It is the symbolic representation of a molecule. |
| It represents one atom of an element. | It represents one molecule of an element or compound. |
| It is written according to the English, Latin or other names of an element. | It is written with the help of symbols and valency of elements. |
| Example: The symbol of hydrogen is H. | Example: Molecular formula of hydrogen is H2. |