Published by: Nuru
Published date: 26 Jun 2021
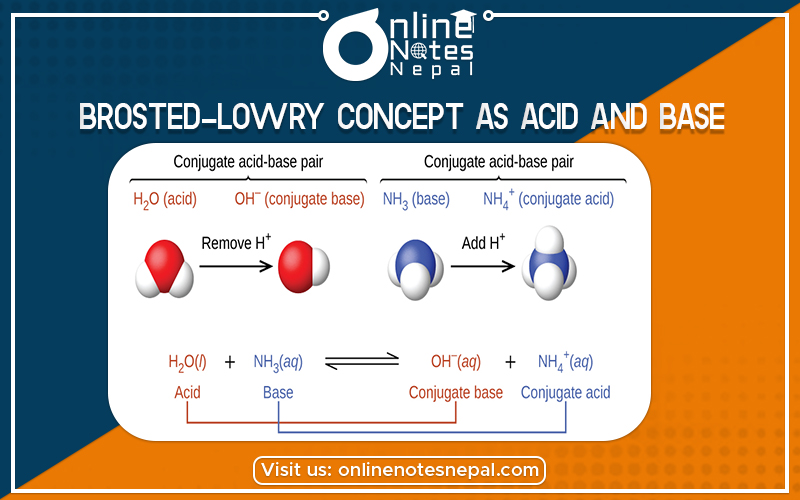
Brosted-Lowry Concept as Acid and Base- The compound which can donate protons or proton donors are called acids.
According to this concept, the compound which can donate protons or proton donors are called acids. Similarly, the compound which can accept the proton or proton-acceptors is called bases.
HCL + H2O CL– + H3O+
In this reaction, HCL acts as an acid because it donates 1 proton while H2O acts as a base because it accepts 1 proton.
According to this concept NH4+, HSo4–, HCO3– etc act as acids because all of them can produce proton.
NH4+ + CH3COO– NH3 + CH3COOH
(acetate ion) (ammonia) (acetic acid)
Conjugate pair- A pair in which one form (i.e. acid or base) is formed from the another either by donating the proton or by accepting the proton is called conjugate pair.
Let us consider the following chemical reaction.
HCL + H2O CL– + H3O+
The base which is produced when an acid donates proton is called conjugate base of the acid. Similarly, the acid which is produced when a base accepts proton is called conjugate acid of base. In the above reaction CL– is the conjugate acid of base.
Advantage of Bronsted-Lowey concept of acid and base
For example:- HCL + H2O CL– + H3O+
(Acid-1) (base-1) (conjugate base-2) acid-2
Limitations of Bronsted-Lowry concept of acid and base
Eg:- CaO + SO3 CaSO4
(Base) (acid) (salt)
Eg:- SO2 + SO2 SO2+ SO3– –
therefore, the Brosted-Lowry Concept as Acid and Base is explained above.