Published by: Nuru
Published date: 25 Jun 2021
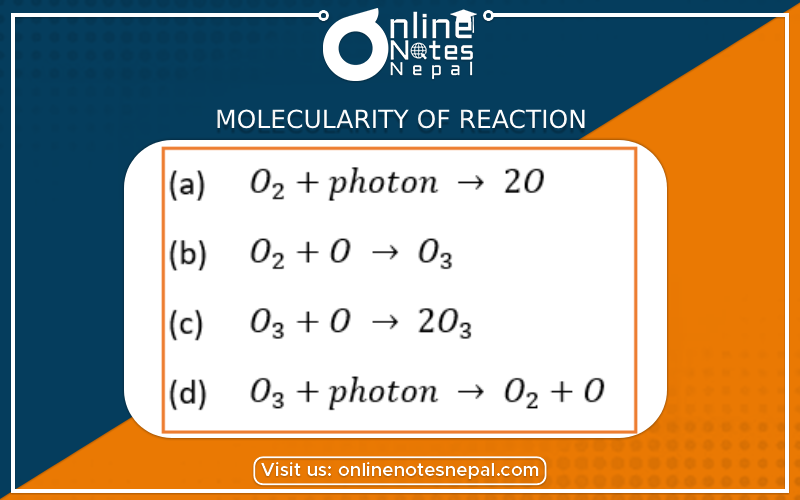
The total number of reactant molecules involved in a chemical reaction by effective collision to form a product under the suitable condition of temperature and pressure is called the Molecularity of reaction.
It is obtained by the sum of coefficients of reactants in the given chemical equation so, it is a theoretical parameter.
Its value is never equal to zero because at zero Molecularity molecule doesn’t exist. The Molecularity of higher-order reaction is difficult to calculate. Depending upon the Molecularity the chemical reaction may be described as unimolecular reaction bimolecular reaction trimolecular reaction and so on.
It is a single molecule of reactant is involved in a chemical reaction then such a type of reaction is called a unimolecular reaction.
N2O5 (g) → 2NO2 (g) + 1/2O2 (g)
If two molecules of reactant are involved in a chemical reaction then such a type of reaction is called bimolecular reaction.
Example:
H2 (g) + I2 (g) → 2HI (g)
If three molecules of reactant are involved in a chemical reaction then such type of reaction is a trimolecular reaction or ter molecular reaction.
Example:
2N0 + O2
The reaction in which molecularity and order of reaction found to be same are
H2O2 (l) → H2O (g) + 1/2 O2 (g)
Molecularity = 1
Rate = K [H2O2]1
Order of reaction = 1
The reaction in which order and molecularity are not the same are:
1) 2NO + 2H2 → N2 + H2O
Rate = K [NO]2 [H2]
Order of reaction = 2 + 1 = 3.
Molecularity = 2 + 2 = 4
2) CHCl3 + Cl2 → CCl4 + HCl
Rate = K[CHCl3]1 [Cl2]1\2
Order of reaction = 1 +1/2 = 3/2
Molecularity = 1 + 1 = 2
3) 2N2 O3 → 4N)2 + O2
Rate = K [N2O5]1
Order of reaction = 1
A chemical reaction that takes place in one and only one step i.e., all that occurs in a single step is called elementary reaction while a chemical reaction occurring in the sequence of two or more steps is called a complicated reaction. The sequence of steps through which a complicated reaction takes place is called the reaction – mechanism. Each step in a mechanism is an elementary step reaction.
The molecularity of an elementary reaction is defined as the minimum number of molecules, atoms or ions of the reactants required for the reaction to occur and is equal to the sum of the stoichiometric coefficients of the reactants in the chemical equation of the reaction.
In general, the molecularity of simple reactions is equal to the sum of the number of molecules of reactants involved in the balanced stoichiometric equation.