Published by: Sujan
Published date: 18 Jun 2021
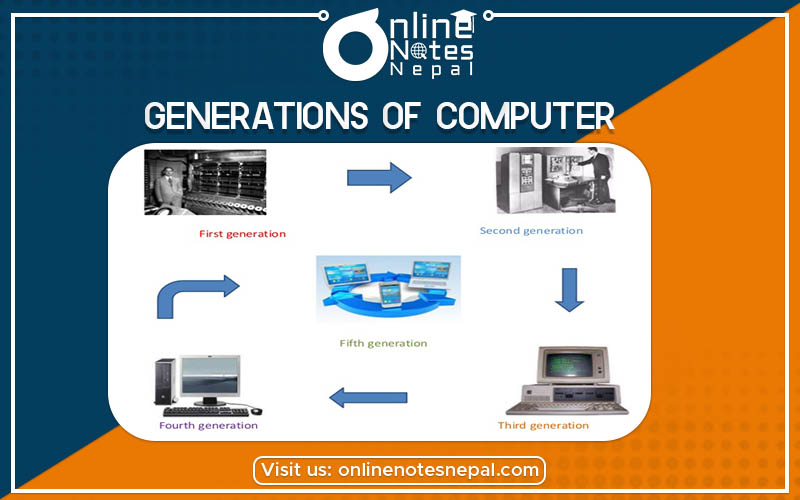
In computer terminology, the word generation describes a stage of technological development or innovation that changed the way of the computer to operate. This also came up with the result in being smaller, cheaper, more powerful, efficient, and reliable devices in each generation of computers. According to the kind of processor installed in a machine, the development of computers is divided into five distinct periods. These are characterized by major technical development. They are:
These computers were very large in size and required huge space for its placement. They were used in scientific applications in the then time. They did not have versatility.
Characteristics:
Examples: ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC, IBM-701, and IBM-650.

Fig: First Generation Computer
These were smaller in size as compared to that of the first one. They had a better probability than the previous one.
Characteristics:
Examples: PDP-8, CDC 1604, IBM 1401

Fig: Second Generation Computer
In this, users interacted through input and output devices such as keyboards and monitors. IC was the main component, made of a thin silicon wafer. They were more portable than the previous generation computers.
Characteristics:
Examples: PDP 11, NCR 935

Fig: Third Generation Computer
The fourth-generation computer is the improvement of the third generation. It uses LSI (Large Scale Integration) as well as VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) technologies. These were more reliable, portable, and cheap. There was an introduction to Multimedia techniques.
Characteristics:
Examples: Intel Core, Apple PCs, IBM PCs, etc.

Fig: Fourth Generation Computer
This generation computer is the best in the computing era. These are still developing and in the future, it will dominate other technologies as well. These are being designed to use AI (Artificial Intelligence) and solve problems on its own. They will estimate the human way of thinking. These will, later on, respond to the natural languages used by us.
Characteristics:
