Published by: Anu Poudeli
Published date: 14 Jul 2023
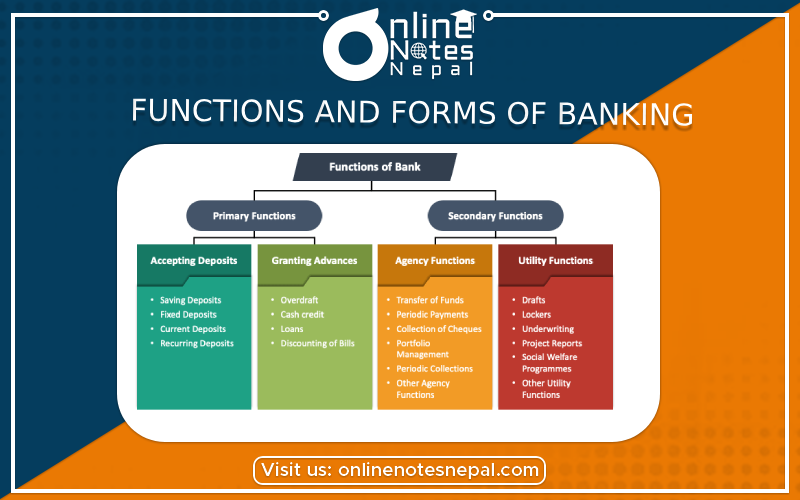
Banking Functions:
Accepting Deposits:
Accepting deposits from individuals, businesses, and other organizations is one of a bank's key functions. Savings accounts, current accounts, fixed deposit accounts, and other types of deposit accounts are available from banks.
Providing loans and Advances :
Banks make loans and advances to individuals and organizations for a variety of reasons, including as purchasing a property, beginning a business, or expanding existing operations. They evaluate borrowers' creditworthiness and levy interest on loans.
Credit Creation :
Credit creation is the ability of banks to produce credit. They do not need to have an exact quantity of money in their reserves for making loans. They can produce new money by issuing credit, so expanding the economy's money supply.
Payment system :
Banks promote the seamless flow of payments across the economy. They offer services such as check clearing, electronic fund transfers, and the issuance of debit and credit cards, making it easier for consumers and businesses to conduct transactions.
Foreign Exchange Services :
Banks provide foreign exchange services, allowing consumers and corporations to convert one currency into another. They make international trade and investment easier by offering services like currency exchange, trade finance, letters of credit, and foreign remittances.
Wealth Management:
Banks offer wealth management services, assisting individuals and organizations in properly managing their financial assets. Investment advice, portfolio management, estate planning, and retirement planning are examples of these services.
Banking Varieties:
Retail Banking:
Retail banks serve individual customers and small businesses. They offer a range of services such as savings and checking accounts, loans, mortgages, credit cards, and basic investment products. Retail banks have a network of branches, ATMs, and online platforms to provide convenient access to their customers.
Commercial Banking:
Commercial banks primarily serve businesses, including large corporations, small and medium enterprises (SMEs), and government entities. They offer a comprehensive range of services, including business loans, trade finance, cash management, treasury services, and corporate advisory.
Investment Banking:
Investment banks assist companies and governments in raising capital through the issuance of securities such as stocks and bonds. They also provide advisory services for mergers and acquisitions, underwriting of securities, and trading in financial markets. Investment banks often work with institutional clients rather than individual customers.
Rather than working with individual clients, investment banks frequently work with institutional clients.
Central Banking:
Central banks are the apex financial institutions of a country or group of countries. They have regulatory and supervisory responsibility over other banks that fall under their jurisdiction. Central banks are in charge of monetary policy, controlling the money supply, ensuring financial stability, and serving as lenders of last resort.
Islamic Banking:
Islamic banks function according to Islamic law (Sharia). They eschew interest-based transactions and invest in an ethical and socially responsible manner. Profit-sharing arrangements, lease-based financing, and trade-based transactions are examples of Sharia-compliant goods offered by Islamic banks.
Online banking:
often known as internet banking or e-banking, enables users to conduct a variety of banking transactions electronically via secure websites or mobile applications. It offers customers convenience and accessibility by allowing them online manage their accounts, transfer payments, pay bills, and apply for loans without having to visit real bank locations.
It is crucial to remember that the specific roles and forms of banking differ by country and are subject to legal frameworks and local banking practices.