Published by: BhumiRaj Timalsina
Published date: 12 Jan 2022
Basically processing hardware is the Central Processing Unit (CPU) of computer system. CPU is the central processing unit of the computer. It process data according to our instructions. Processing is a procedure that transforms raw data into meaningful information.
It is a part of CPU where all the given instructions, data and the results are stored during processing period. By using the unique address we can identify the locations of memory. There are different types of memory among them the popular are RAM (random Access Memory), ROM (Read Only Memory). Memory refers to the electronic holding place for instructions and data where the computers microprocessors can reach quickly. Computers need memory to store data and process them. We can represent the memory to store the data and process them. We can represent the memory using different units like 8 Bits = 1 byte (One Character) 1024 Byte= 1 Kilo Byte (KB) 1024 KB= 1 Mega Byte (MB) 1024 MB= 1 GB (Giga Byte) 1024 GB= 1 TB (Tera Byte)
Basically we have two types of memory used on computer system. These are primary memory which is known as main memory or internal memory or simply memory and the secondary memory which is known as auxiliary memory or backup storage or external memory. Besides these two memories we have internal processor memories like cache memory, register, virtual memory etc.
The CPU contains the basic instructions needed to operate the computer, but it doesn't have the capability to store entire programs or data permanently. The CPU contains registers, but these are small areas that can hold only few bytes of data at a time. However, the CPU needs to have millions of bytes of space to hold programs and the data being manipulated.
Physically, memory consists of chips either on the motherboard or on a small circuit board attached to the motherboard. There are two types of memory:
RAM (Random Access Memory)
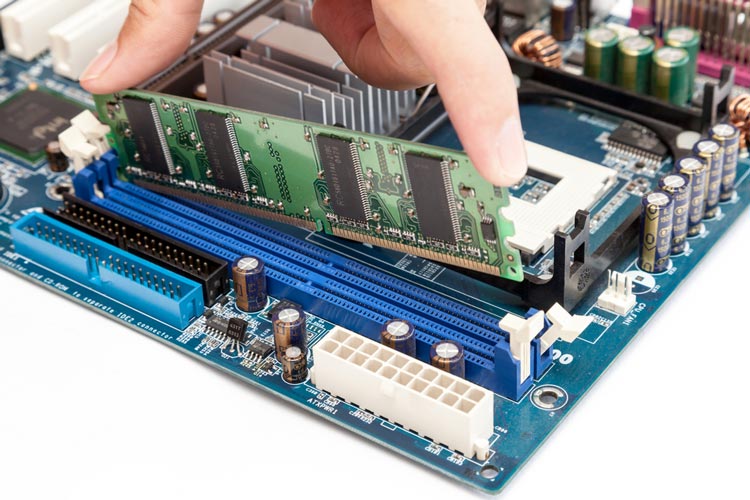
By memory, we generally mean RAM which is volatile in nature. It is a high speed memory that holds programs and data only when use. It requires constant supply of power. It is also called Read/Write Memory or volatile memory. The most important factor affecting the speed and power of a computer is the amount of RAM it has. The more RAM in a computer, the more it can do. The measuring unit of memory is byte, which is the amount of memory required to store a single character. RAM has the ability to access each byte of data directly, so it is named Random Access Memory. There are two types of RAM: SRAM (Static RAM) and DRAM (Dynamic RAM).
ROM (Read Only Memory)

These are non-volatile chips always holding the same data. Data in them can't be changed, that is, the contents in ROM cannot be written or erased by the user; these are 'hard-wired' or done only once by the manufacturer, hence they called Read Only Memory or sometime called permanent. Generally, ROM contains system programs for handling the operating system. There are different types of ROM: Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM), Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EPROM), and Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM).

These are used to store large volume of data permanently for the future use. These are non-volatile in nature. These are less expensive, so most computers have a large amount of secondary storage. However, they don't operate as fast as primary memory such as RAM. Secondary storage devices are often referred as back-up memory or external memory or additional memory. There are two types of secondary memory. They are: