Published by: Anu Poudeli
Published date: 30 Jul 2023
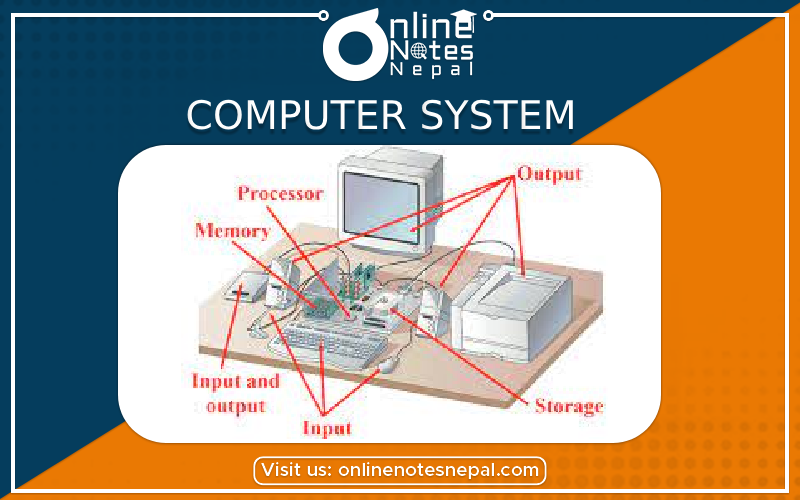
Let's take a look at the main components of a computer system: the Central Processing Unit (CPU), memory, and storage systems.
CPU (Central Processing Unit):
The Central Processing Unit is commonly referred to as the computer's brain. It is in charge of processing instructions and conducting calculations for all computer processes. The CPU is in charge of data processing and the overall operation of the computer system. It is made up of various parts, including:
Memory:
RAM (Random Access Memory) is where the computer stores data and instructions that the CPU needs to access rapidly. RAM is volatile, which means that its contents are lost when the computer is turned off. RAM is used by the CPU to load and run applications, processes, and data that are actively in use.
RAM provides faster data access than storage devices (e.g., hard drives, SSDs), but it is less capacious and more expensive. It is measured in gigabytes (GB) or terabytes (TB), and having more RAM helps a computer to manage larger datasets and run more apps concurrently without experiencing severe slowdowns.
Storage Devices:
Storage systems in computers are used to persistently store data and programs even when the power is switched off. Storage systems are classified into two types:
Other types of storage systems, such as optical drives (e.g., CDs, DVDs) and external storage devices (e.g., USB flash drives, external hard drives), provide portable storage alternatives.
To summarize, the Central Processing engine (CPU) is the computer's primary processing engine, whereas memory (RAM) provides rapid temporary storage for currently used data. Storage devices, such as hard drives and solid-state drives (SSDs), provide permanent storage for programs, files, and data even when the computer is turned off.