Published by: BhumiRaj Timalsina
Published date: 20 Jan 2022
A business performs a large number of financial transactions daily. It purchases goods from suppliers and sells to its customers. It returns well to suppliers. It receives goods returned by its customers. It deposits cash in the bank and withdraws from the customers. It pays for expenses like salary, rent, stationery, advertisement and insurance premium. It borrows loan and returns it on maturity. The transactions should be recorded immediately in memorandum books and when they take place. The memorandum book is also called waste book or rough book. It is treated as a temporary record of these transactions, which helps to prepare journal. In fact, the journal is the first step of the accounting process.
Journal is the first book to keep a systematic record of all the business transactions. It is the first entry of all the financial transactions. It is the original book or primary book in which the financial transaction is first recorded in order of date and helps to maintain the principal book or ledger. It is the book of prime entry in which each and every transaction is registered showing debit and credit aspects with a brief explanation called narration.
The following are the main definition of journal:
"A journal is a book, employed to classify or sort out transactions in a form convenient for their subsequent entry."-L.C. Cropper
"The journal or daily record as originally used was a book of prime entry in which transactions was copied in order to date from a memorandum or waste book. The entries as they were copied were classified into debits and credits, so as to facilitate they're being correctly posted afterwards in the ledger."-R. N. Carter.
The main objectives of journal are given below:
The financial transactions are first of all recorded in the journal. The process of recording the financial transactions in the journal in a systematic way is called journalizing. The record of the transactions made in the journal is called journal entry. Journalizing is the act of passing journal entry. The following steps are taken into consideration while journalizing the transactions:
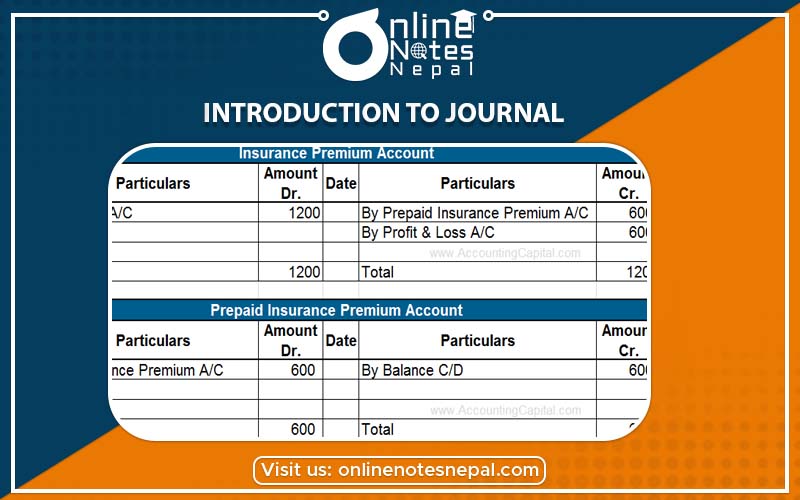
According to the double entry system, every transaction is recorded in the journal involving its two aspects. One aspect of the transaction is debited in one account and the other aspect is credited in another account involving the equal amount. The crucial task while journalizing the transaction is to decide the account to be debited and credited. The system record of a transaction in the journal book is called journal entry, the process of passing journal entry is called journalism.The rules are also known as rules of debit and credit.
1. Personal Account: It is the account of a person or organization or debtor or creditor. It is the record of an individual or organization. Under it, the person receiving the benefit is debited and the person giving benefit is credited. The rule of journalizing in personal account is as follows:
2. Real Account: It is an impersonal account. It is the account of a real thing or property. It is the record of assets of the business. Under, it asset coming into the business through its purchase is debited and the asset going out of the business through its sale is credited. The rule of journalizing in real account is as follow:
3. Nominal account: It is another impersonal account. It is the account of expenses, loss, income, and profit. It has no any physical shape. It does not exist in the business in real form. It appears only in the books. It is the record of financial sacrifice against the service received and the record of financial benefit against the service rendered. The rule of journalizing in nominal account is as follows: